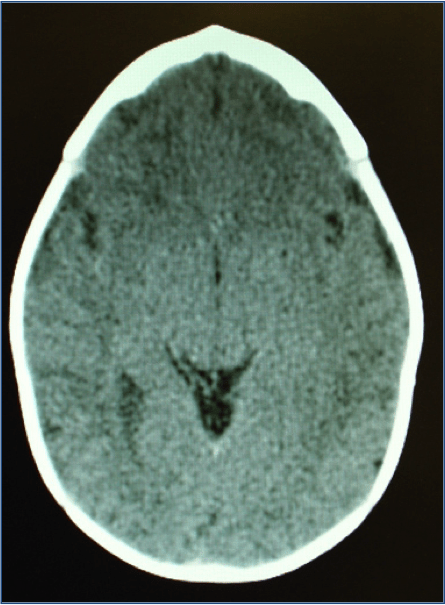
Craniosynostosis refers to a premature closure of cranial suture(s). Its incidence ranges from 1/1,800 to 1/2,500 live births. I can either be isolated or involve multiple suture. It is also classified as Non-syndromic vs. Syndromic.
Sagittal synostosis is most common, metopic comes 2nd with increasing incidence: 1:10000 live births vs. 1:15000 live births for unicoronal synotosis.
There are various pertinent reasons that justify the surgical treatment of craniosynostosis
- Dysmorpholgy of the skull, orbits and face – leading to important psychosocial problems
- Intracranial Pressure
- When measured with invasive intracranial monitoring devices
- Non-syndromic: up to 19% increase in ICP
- Syndromic: up to 47 % increase in ICP
- Chiari malformation (seen in conjunction with increased ICP and felt to be caused by a disproportion between hindbrain growth and an abnormally small posterior fossa)
- Neurodevelopmental and intellectual delay
- Airway compromise seen in craniofacial syndromes
- Ocular/visual compromise
- Due to soft tissue/bony anomalies, leading to proptosis and placing the globe at risk for exposure keratitis and ulceration
- Irreversible optic nerve atrophy can also be the result of intracranial hypertension
- Amblyopia and ametropia
Visit your Craniofacial Surgeon if you have any question with regards to the shape of your baby’s head. Craniosynostosis can be misdiagnosed for positional plagiocephaly. The diagnosis is a clinical one. No imaging is usually necessary to make a diagnosis.